Search Mashup tool 🔍
Use the Search Mashup tool to enable AI-powered workflows to search and retrieve content from your VIDIZMO content library. When you connect this tool to an AI node, the AI model can dynamically query videos, documents, images, and other media based on user input and workflow context.
In this article, you learn how to add, configure, and test the Search Mashup tool in your workflow.
Concept
The Search Mashup tool is a VIDIZMO-specific tool node that provides AI models with access to your content library. Unlike regular workflow nodes that execute in sequence, this tool is invoked by an AI node only when the model determines that content retrieval is needed.
Key Capabilities:
- Keyword and semantic search - Find content by title, description, or vector embeddings
- Content filtering - Filter by format, status, author, tags, and custom attributes
- Date-based queries - Search within specific date ranges for creation, publication, or modification
- Feature-based filtering - Filter by transcription, AI processing, and other content features
- Pagination support - Control result size and navigate through large result sets
Understand How the Tool Works
This section explains how the Search Mashup tool operates within a workflow and how it connects to other nodes.
Tool Connectors
In the Workflow Designer, nodes use colored connectors to indicate the type of connection and data flow. The Search Mashup tool uses the green connector, which is specific to tool nodes.
Green Connector Behavior
The green connector distinguishes tool nodes from regular workflow nodes:
- AI-driven Invocation - Tools connected through green connectors don't execute automatically in sequence. The AI node decides when to invoke them based on user input and context.
- On-demand Execution - The Search Mashup tool executes only when the AI model determines that content search is required.
- Multiple tools Support - An AI node can have multiple tools connected through green connectors. The AI model selects which tool to use based on the task.
Execution flow
When a workflow runs, the Search Mashup tool operates in this sequence:
- The AI node receives user input from the chatbot.
- The AI model analyzes the input and determines whether content search is needed.
- If search is needed, the AI invokes the Search Mashup tool through the green connector.
- The tool builds a search request using configured parameters and resolves dynamic values from
state.data. - The VIDIZMO API executes the search with the user's authentication context.
- Search results are stored in the field specified in Output Field.
- The AI node accesses the results and generates a response for the user.
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ User Query │ ───► │ AI Node │ ───► │ Search Mashup │ ───► │ VIDIZMO API │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ │ (Green Connector)│ └──────────────┘
▲ └──────────────────┘ │
│ │
└────────── state.data.search_results ◄─────────┘
When to Use This Tool
Use the Search Mashup tool when your workflow requires:
- AI-driven content discovery based on natural language queries
- Dynamic retrieval of videos, documents, or media assets
- Responses grounded in your organization's content library
- Contextual search filtering based on conversation state
Add the Search Mashup Tool to Your Workflow
Follow these steps to add the Search Mashup tool to your workflow canvas.
-
Go to Portal Settings > Chatbot > Workflow.
-
Select an existing workflow or create a new workflow.
-
In the Node Library, expand the VIDIZMO or Tools category.
-
Drag Search Mashup Tool onto the canvas.
Connect the tool to an AI node
After you add the Search Mashup tool to the canvas, connect it to an AI node.
-
Locate your AI node (such as an LLM node) on the canvas.
-
Drag a connection line from the green connector to the input connector on the Search Mashup tool node.
-
Release to create the connection. A green connector (●) indicates a successful tool connection.
NOTE: The green connector indicates that the tool is available to the AI node for on-demand invocation. The tool doesn't execute in sequence with other nodes,it executes only when the AI model decides to invoke it.
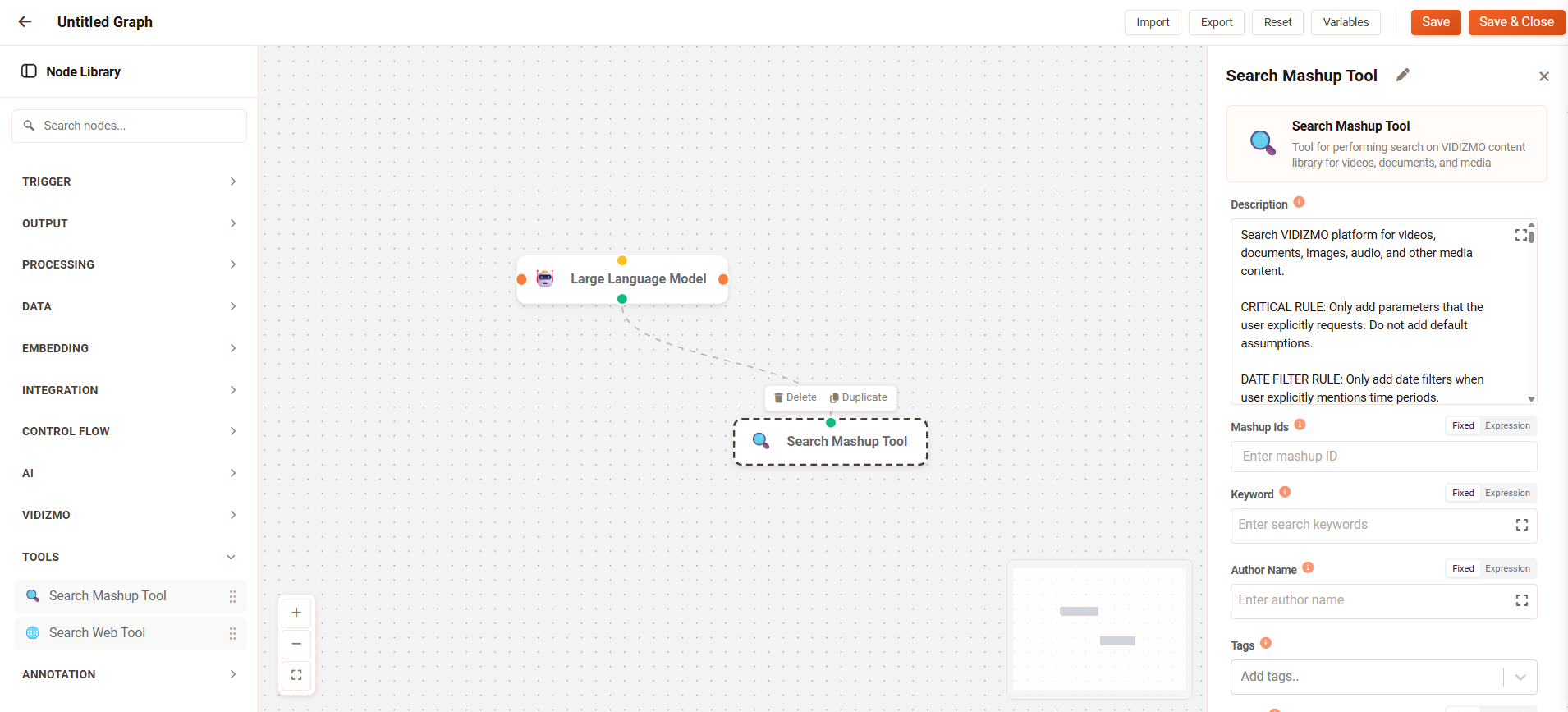
Configure the Search Mashup Tool
Select the Search Mashup node to open the Node Configuration Panel. You can configure the following options:
Description
Instructions for the LLM on how and when to use this tool. The default description provides comprehensive guidance including:
- Core parameter mappings for keyword, author, content types, and status filters
- Date filter rules with UTC ISO format conversion examples
- Valid enum values for content types, status, and other filters
- Example queries showing which parameters to use for different user requests
The AI uses this description to determine which search parameters to populate based on user queries. For example, when a user asks "show me videos from last week," the AI reads the description to understand it should set mashup_formats=["Video"] and add the appropriate date filter.
TIP: Keep the default description unless you need to customize the AI's search behavior for specific use cases.
Search Parameters
You can configure the following search options:
-
Mashup IDs: Unique numeric identifiers to retrieve specific content items directly. Use this when you need to fetch known content by ID rather than searching. Enter one or more IDs separated by commas. For example, enter
12345as a fixed value, or use${state.data.target_mashup_id}to reference a variable containing the ID. -
Keyword: Search terms that match against content titles and descriptions. The AI typically populates this from user queries like "find marketing content" or "search for project reports." Enter static terms like
workplace safetyor use${state.data.system.user_query}to dynamically use the user's input. -
Author Name: Filter content by the creator's name. Use this when users ask for content from a specific person, such as "John's videos" or "content by Sarah." Enter a name like
John Smithor reference a variable like${state.data.author}. -
Tags: Array of tag strings to filter content by category labels. Select Add tags to choose from available tags in your library or enter custom values. For example, add tags like
training,safety, oronboardingto narrow results to categorized content. -
Vector: Named vector for semantic similarity search. This enables finding conceptually related content even when exact keywords don't match. Reference a vector object generated by an Embedding node—the object must contain
nameandvectorfields. For example, use${state.data.query_embedding}to reference embeddings created from the user's question.
All search parameters support Fixed (static value) and Expression (dynamic value using ${variable} syntax) input modes.
Content Type Filters
-
Content Types: Restricts search results to specific media formats. Select one or more types from the dropdown: Video, Audio, Document, Image, Live, Collection, or Playlist. When a user asks for "videos about training," the AI sets this to Video. Leave empty to search all content types.
-
Timed Data Types: Filter media by the type of timed metadata present, such as transcripts, chapters, or other time-based metadata. Use this to find content that has specific metadata available for search or display.
-
Include Nested Mashups: When enabled, includes child items from collections or playlists in search results. Enable this when searching within collections and you want all nested content returned. Disabled by default.
Feature Filters
-
Is Featured: When enabled, returns only content marked as featured in your library. When disabled or unchecked, returns all content regardless of featured status. Use this when users specifically ask for "featured content" or "highlighted videos."
-
Has Transcription: When enabled, returns only content with captions or transcripts available. When disabled or unchecked, returns all content. Use this when users need searchable or accessible content with text alternatives.
-
AI Processed: When enabled, returns only content that has been processed by AI services (such as AI-generated summaries, tags, or insights). When disabled or unchecked, returns all content. Use this when users ask for "AI-enhanced content" or need content with AI-generated metadata.
Date Range Filters
Filter content by creation or publication dates. All dates use ISO 8601 UTC format (YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ).
-
Added From Date: Content creation start date. Returns content added to the library on or after this date. Use when users ask for content "uploaded since yesterday" or "added last week."
-
Added To Date: Content creation end date. Returns content added to the library on or before this date. Combine with Added From Date to define a specific upload window.
-
Published From Date: Publication start date. Returns content published on or after this date. Use when users ask for "recently published" content or content "published this month."
-
Published To Date: Publication end date. Returns content published on or before this date. Combine with Published From Date to define a specific publication window. Use the date picker for fixed values, or expressions for dynamic values like
${state.data.start_date}. The AI automatically converts relative dates from user queries (e.g., "last week" becomes2024-12-15T00:00:00Z).
Output Settings
-
Max Results: Maximum number of search results to return. Enter a value between 1 and 1000. Default is 20. Use lower values (10-20) for faster responses in conversational agents. Use higher values when comprehensive results are needed.
-
Mashup Search Parts: Specifies which data parts to include in each search result. Select from: BasicInfo (title, description, dates), TimedData (transcripts, chapters), Content (full content data), and PlaybackUrl (URLs for playback). Defaults to all parts if not specified. Select only the parts you need to reduce response size.
-
Output Field: Variable name where search results are stored for use by other nodes. Click to select an existing variable or create a new one. The AI node and subsequent workflow nodes access results using
${state.data.<variable_name>}. For example, if you name itsearch_results, access it as${state.data.search_results}.
Test the Configuration
After you configure the Search Mashup tool, test the workflow to verify correct behavior.
-
Go to Portal Settings > Chatbot > Agents.
-
Select the agent associated with your workflow, or create a new agent and assign your workflow.
-
Open the chatbot interface in the portal.
-
Enter a query that should trigger content search. For example:
- "Find videos about onboarding"
- "Show me documents uploaded last week"
- "What training content do we have?"
-
Verify that the agent returns relevant content from your library.
-
Check that results match your configured filters and parameters.
-
If results don't match expectations, return to the Workflow Designer and adjust your configuration.
Supported Values Reference
Content Types
Use these values for the Content Types parameter:
- Video - Video content
- Audio - Audio content
- Document - Document files
- Image - Image files
- Live - Live streaming content
- Collection - Content collections
- Playlist - Playlists
Status Values
Use these values for status filtering:
- Published - Published and visible content
- Drafted - Draft content not yet published
- Archived - Archived content
- Pending For Approval - Content awaiting approval
Publishing Status Values
Use these values for publishing status filtering:
- Current Published - Currently published content
- Expired - Expired content
- Future Published - Scheduled for future publication